By: DR. AZIZUR RAHMAN
Skin cancer occurs when skin cells grow abnormally on the skin exposed to the sun. The key areas to focus on are the face, arms, chest, and hands. Yet, it may also impact regions of the skin that have had limited sunlight exposure. The following areas include the lips, scalp, neck, soles of the feet, ears, genitals, and beneath your fingernails or toenails. Initially, skin cancer manifests as freckles, moles, or spots on the skin.
Types of skin cancer
The different types of skin cancer are as follows:
Melanoma is considered the most severe form of skin cancer. It transforms melanocytes into cells that produce melanin. Non-melanoma skin cancer includes all types of skin cancer that are not melanotic. The treatment for this cancer varies depending on the type of cancer, whether it is basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. Both of these cancer types are classified as non-melanoma skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is a form of skin cancer originating in the basal cells. Basal cells in the skin generate new skin cells as old cells perish. One can easily spot this cancer as a clear bump on the skin. However, it can manifest in various ways. It typically appears in regions that receive the most sunlight, like the head and neck.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is the more prevalent form of skin cancer. It arises in the squamous cells that produce the middle and outer layers of the skin. Although cancer can be aggressive, it is not necessarily life-threatening. When cancer is not treated, it can spread to different areas of the body and increase in size, leading to severe complications.
Causes of skin cancer
Skin cancer may develop due to mutations or defects in the DNA of skin cells. The alterations lead to the cells becoming unmanageable and forming a mass. Numerous cell types are implicated in skin cancer. The epidermis is located on the top layer of the skin. The epidermis forms a thin layer that acts as a protective barrier against skin cells being constantly shed from the body. There are three different types of cells present.
Squamous cells are located just below the outer surface. They serve as the inner lining of the skin.
Basal cells are located beneath the squamous cells. New skin cells are produced.
Melanocytes produce melanin, a pigment in the skin responsible for normal coloration. Cells can be found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanocytes shield the deeper skin layers by generating melanin in response to increased sun exposure.
Other reasons
UV radiation from sunlight and tanning beds can cause significant damage to the DNA of skin cells. Other factors also play a role in increasing the risk of skin cancer. These factors may include conditions that compromise the immune system or exposure to toxins.
Symptoms of skin cancer
Skin cancer typically originates in areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to sunlight, including the scalp, ears, chest, face, neck, lips, hands, and arms. It may also manifest in the legs of women. It can appear on the hands, toenails, under the nails, and genitals.
Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma – It most commonly occurs on your neck or face. Cancer appears as a waxy or pearly bump. It appears as brown spots or flesh-colored lesions or as scabbing or bleeding sores that return to healing.
Symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma – It appears on the ears, face and hands. People with dark skin are at higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma. It appears as a red, firm nodule. It may appear as a flat lesion with a grooved, raw surface.
Symptoms of Melanoma – Melanoma can develop on existing moles on your body that can become cancerous or normal skin. It occurs in the mouth or even the trunk of affected males. Melanoma usually develops on the lower legs in women. Melanoma affects areas of skin with minimal sun exposure in both men and women. It appears on the palms and soles of people with acne-prone skin. Symptoms of melanoma are:
A mole that is bloody or changes in size, color and feel.
A painful sore that burns or itches.
A large brown spot with dark freckles.
Dark lesions on nails, nose, anus or vagina, fingernails or toes, hands.
A lesion that appears red, white, pink, blue, or blue-black with irregular borders.
skin test
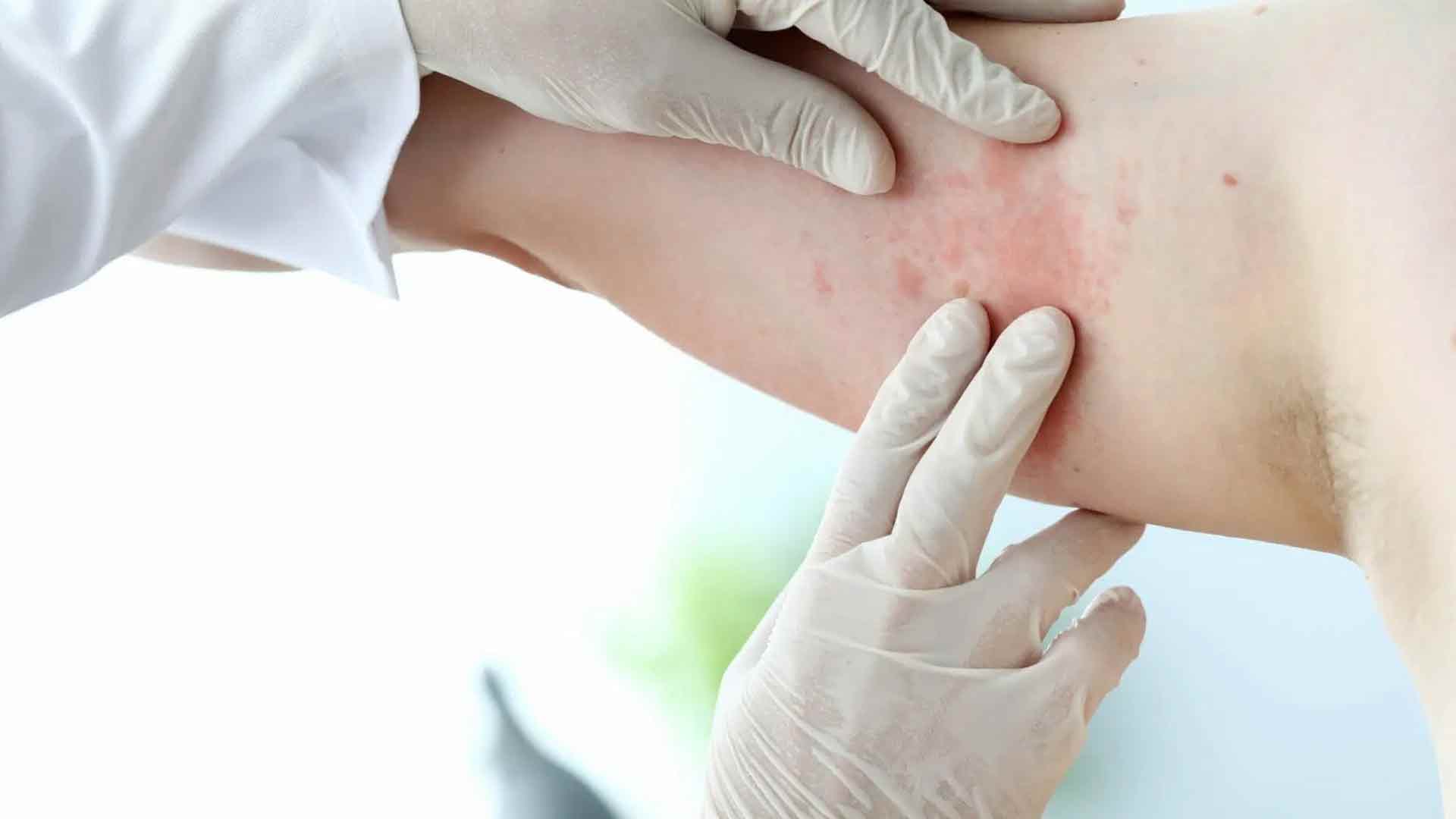
Doctor may examine your skin for changes that may indicate skin cancer. However, further tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Skin biopsy
Doctor may look for suspicious skin. He or she may remove this section of skin for laboratory testing. A biopsy determines whether you have skin cancer. Yes, he is cancer to you Can tell the type of
Skin cancer treatment options
Treatment options for malignant skin lesions and skin cancer vary. It depends on the type, size, location and depth of the lesions.
Freezing
Doctor can freeze skin lesions, such as actinic keratoses or some early cancers, to destroy them. Liquid nitrogen is used in this method. When it is dissolved, the dead tissue becomes sluggish.
Excisional surgery
Mole Excision Image
This treatment requires excision (cutting) of the cancer with an edge of the surrounding healthy skin.
Radiation therapy
Radiation Image
The therapy uses X-rays to kill cancer cells.
chemotherapy
This therapy uses drugs to kill cancerous cells. Your doctor may prescribe creams or lotions with anticancer agents to apply to the skin for upper-layer skin cancer.
Biological therapy
This therapy requires the use of the body’s immune system to completely kill the cancer cells.